What is HSCT?
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, commonly known as a stem cell transplant, is a medical procedure where healthy blood stem cells are transfused into a patient to restore bone marrow and immune system function after the patient's bone marrow is damaged or destroyed by disease, radiation, or chemotherapy.
Types of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
There are two main types of HSCT:
Autologous stem cell transplant
In an autologous Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) , a patient's own stem cells are collected from their bone marrow or peripheral blood before undergoing high-dose chemotherapy or radiation therapy. The high doses are meant to destroy any remaining cancer cells or marrow abnormalities. The collected stem cells are then returned to the patient after treatment to help the bone marrow recover and start producing new blood cells. Autologous transplants are typically used to treat several types of cancer.
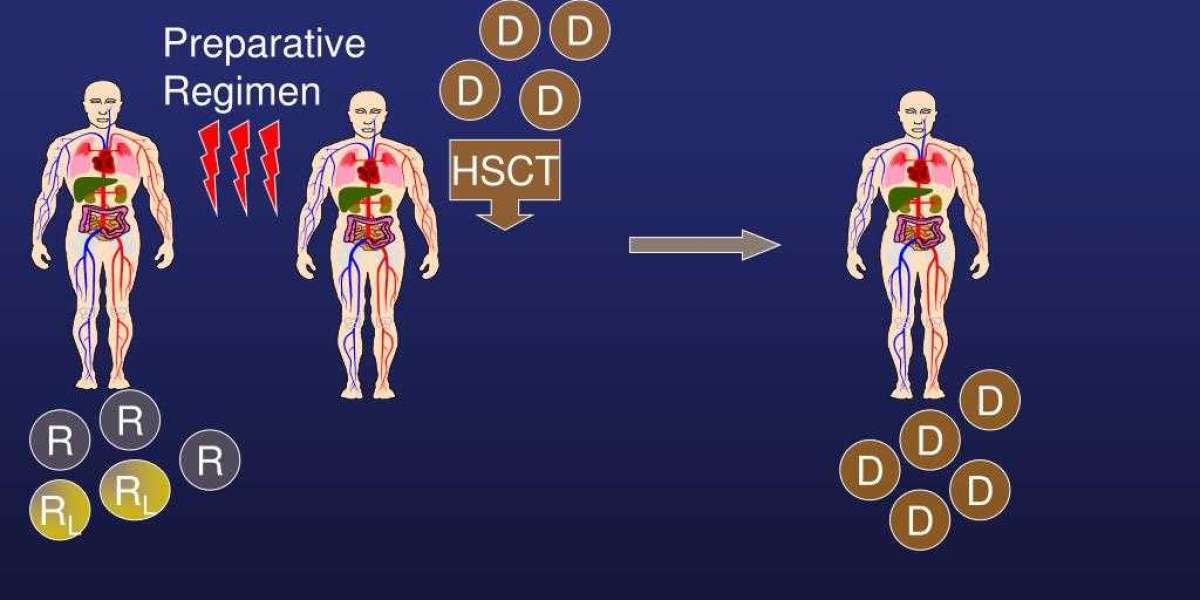
Allogeneic stem cell transplant
In an allogeneic transplant, stem cells are collected from a donor whose tissue type closely matches the recipient's. This is usually a sibling who is a genetic match but can also come from an unrelated donor. Allogeneic transplants are more complex than autologous transplants because the donor's cells see the recipient as foreign, so special immunosuppressive drugs must be given to prevent rejection. Allogeneic transplants are used to treat conditions like leukemia, lymphoma, and genetic diseases affecting the bone marrow. They have the potential to provide a cure by replacing the defective marrow with healthy donor cells.
Get More Insights on- Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT)
For Deeper Insights, Find the Report in the Language that You want: