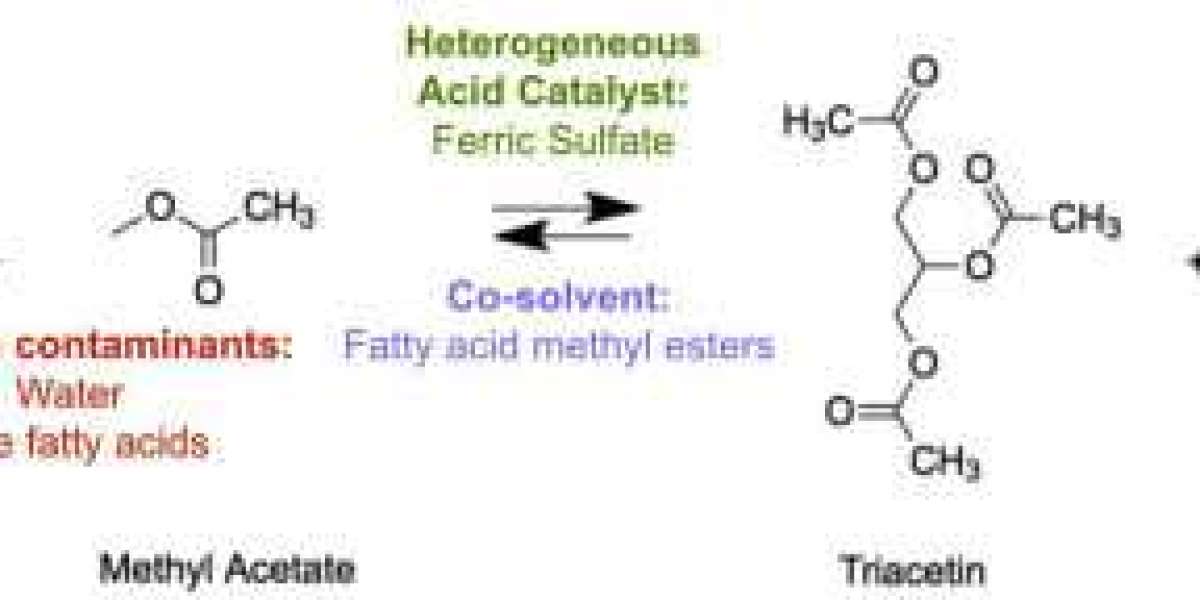
Formation and Structure
Fatty acid esters are compounds formed by a condensation reaction between a fatty acid and an alcohol. This reaction involves the fatty acid's carboxyl group reacting with the alcohol's hydroxyl group, removing a water molecule and forming an ester bond. The alcohol involved is typically a monohydric alcohol like methanol, ethanol, or glycerol.
The Fatty Acid Ester of a fatty acid ester consists of a hydrocarbon chain backbone with a carboxyl group at one end and an ester group at the other. The length and degree of saturation of the hydrocarbon chain varies depending on the type of fatty acid. For example, esters formed from saturated fatty acids like palmitic acid contain saturated hydrocarbon chains, while esters from unsaturated fatty acids like oleic acid possess one or more carbon-carbon double bonds.
Get More Insights On, Fatty Acid Ester