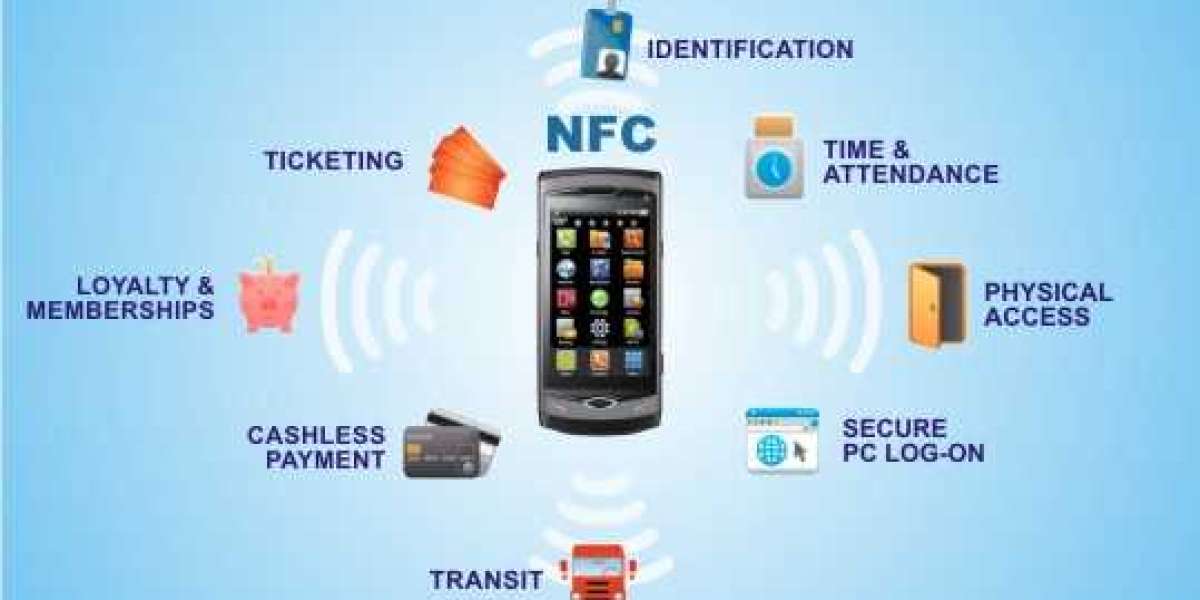
NFC, or Near Field Communication, is a short-range wireless connectivity standard that allows communication between devices when they are touched together or brought within a few centimeters of each other. NFC operates at 13.56 MHz and with a maximum range of 20 centimeters. Some key things to know about NFC include:
- Works with existing infrastructure - NFC uses existing contactless card infrastructure and standards like ISO 14443 and FeliCa. This enables interoperability between a variety of NFC devices and readers.
- Peer-to-peer mode - Near Field Communication allows two active devices to communicate with each other in peer-to-peer mode without any other infrastructure like routers or access points. Data can be exchanged at rates up to 424 kbps.
- Card emulation mode - NFC devices can emulate contactless smartcards and thus can be used for payment and ticketing by operating as a passive target for readers initialized by a third-party. This allows phones to be used like debit or credit cards at payment terminals.
Get More Insights On, Near Field Communication